Our body has a remarkable way of healing itself when hurt or injured. But as we age and develop chronic illnesses or other medical conditions, it can become harder for the body to recover naturally.
For the past few decades, bio-scientists and researchers have used technological advances to find innovative ways to help the body self-heal. Regenerative medicine emerged as a viable resource to support the body in this endeavor.
What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a specialized field of study that focuses on reigniting the body’s natural healing powers to repair or reproduce tissues and organs damaged by diseases, injuries, or aging. Regenerative therapy aims to restore normal function within the body rather than just managing the pain or illness.
Why Are Stem Cells Important to Regenerative Medicine?
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) explains that stem cells are the “repair system” within the body responsible for developing and restoring organs and tissues.
Stem cells play a significant role in supporting the body to renew injured tissues and repair functions the body can no longer fix on its own.
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have no role in the body. However, they can self-renew and differentiate (or change) into various specialized cells that serve a specific function in the body, like fat, blood, brain, or muscle cells.
Stem cells differentiate based on their potency. Cell potency is the differing degree stem cells have to modify into specialized cells: the more specialized cell types, the greater the potency.
Here are three sources of stem cells and their potency:
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs) come from an early-stage embryo (late blastocyst stage). ESCs are pluripotent stem cells, meaning they can transform into any cell type within the body.
- Adult Stem Cells (ASCs) are scarce. They can be found in certain areas of the body, such as the skin, muscle, blood, heart, and brain. ASCs are multipotent, meaning they can only modify into one particular cell type. For instance, a heart stem cell can only help regenerate various cells related to the heart but no other organs.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSCs) come from adult cells, such as the skin or blood cells, that get changed back into the pluripotent state. This process allows the cell to transform into any cell type and helps regenerate any cell in the body.
Types of Regenerative Therapy
Regenerative medicine is a relatively new field (only a few decades old) with endless possibilities to transform and further advance the healthcare industry. Intensive research continues as researchers look for new ways regenerative therapies can help fight diseases, regrow organs, and possibly revert aging.
Here are three types of regenerative therapies used today:
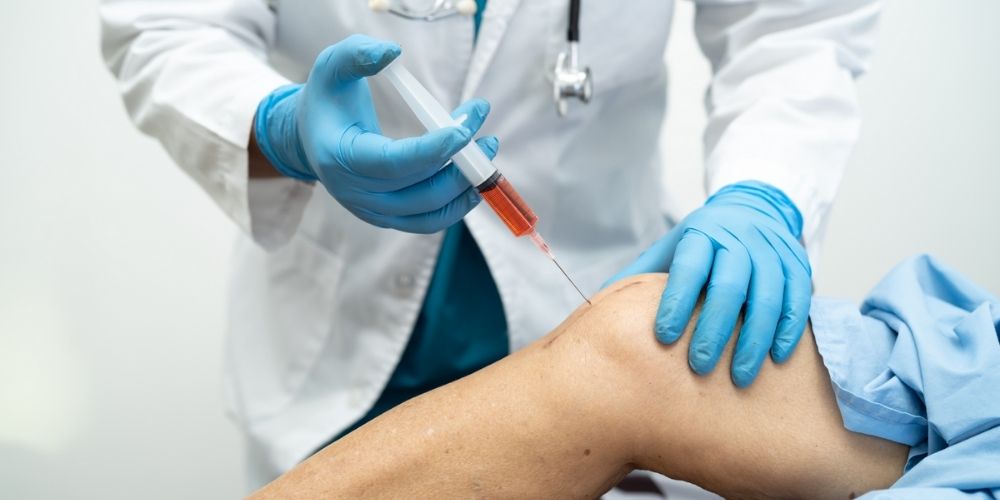
- Stem Cell (SC) – SC therapy uses stem cells collected from the patient’s blood, fat, or bone marrow. It is then injected into the injured area to help the body repair (or rebuild) the damaged tissues. There are little to no side effects from this therapy since the cells come from the patient. Stem Cell therapy can treat conditions like orthopedic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disease.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) – PRP uses blood drawn from the patient. The blood gets purified in a centrifuge and turned into a concentrated solution containing heavier amounts of platelets (a clotting agent). This platelet-rich solution is injected into the affected area to accelerate healing. Platelet-Rich Plasma treats various medical conditions such as joint and muscle injuries, tendinitis, and arthritis. It can also be used for aesthetic treatments, like hair and skin rejuvenation.
- Amniotic Fluid (AF) Allograft – AF Allograft treatments use amniotic fluid taken from healthy Caesarean donors (allograft) rather than the patient. All donated tissues are screened using stringent FDA requirements and guidelines. Amniotic fluid contains hundreds of growth factors and cytokines associated with soft tissue regeneration. These growth factors and cytokines promote healing and pain management when injected into the body. Like PRP, amniotic injections can be used almost anywhere on the body. Amniotic fluid can help treat medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, joint and back pain, ligament injuries, and degenerative disc disease.
Is Regenerative Medicine Covered By Insurance?
Most insurances may cover regenerative injections for PRP and Amniotic Fluid for conditions such as chronic diseases, joint and back pain, muscle and tendon injuries, and osteoarthritis. However, they may not provide coverage for stem cell therapy or PRP injections used for skin and hair rejuvenation. Most likely, these services will be an out-of-pocket expense.
Be sure to check with your insurance provider to confirm the types of services they cover, the level of coverage they provide, and the cost of your deductible.
Learn How Regenerative Therapy Can Help You
At Mason Park Medical Clinic, Katy, TX, we focus on treating the root cause of pain and illnesses so our patients can live fuller and healthier lives.
If you suffer from chronic pain or inflammation, call us at (281) 646-0740 to schedule a consultation to discuss which regenerative therapy is right for you. We look forward to helping you retake control of your health.